The Usage of Gold in Technology and What is Beyond
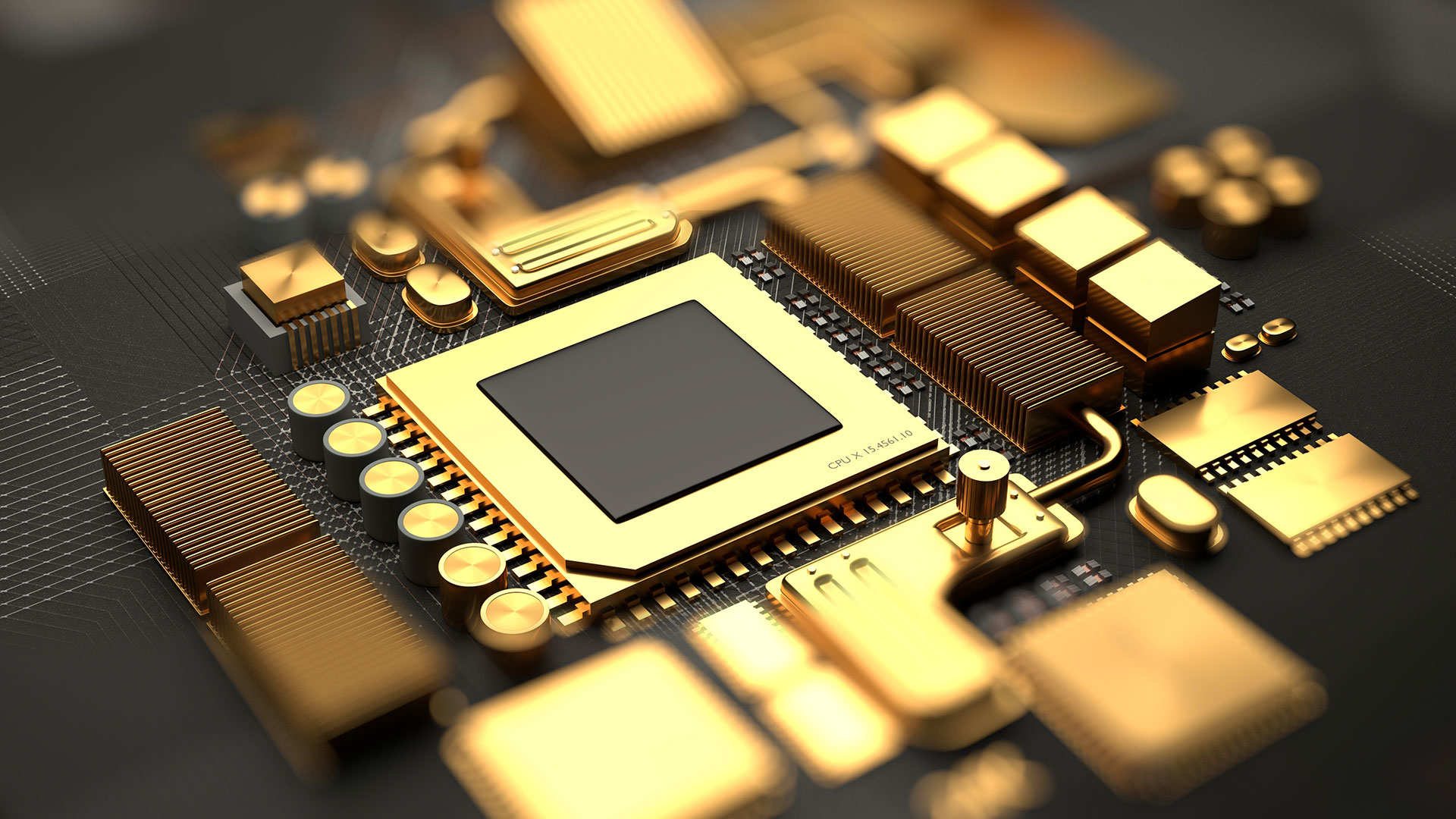
While most people associate gold with jewelry and monetary value, this precious metal plays a crucial role in modern technology. Its unique physical and chemical properties make it invaluable in various technological applications, from everyday consumer electronics to cutting-edge medical devices and aerospace technology.
The Golden Properties:
Gold's prominence in technology stems from its exceptional characteristics. As one of the most malleable and ductile metals, gold can be stretched into wires one-fifth the width of a human hair or hammered into sheets just a few atoms thick. Its outstanding electrical conductivity, coupled with its resistance to corrosion and oxidation, makes it an ideal choice for electrical connectors and contact points in electronic devices.
Is the electronics industry the primary consumer?
The electronics industry is the largest industrial user of gold, consuming approximately 320 tons annually. In smartphones alone, each device contains about 50 milligrams of gold, primarily in the circuit boards. Gold's resistance to corrosion ensures that electronic components maintain reliable connections throughout their lifetime, while its excellent conductivity enables rapid and efficient signal transmission.
Gold is particularly crucial in components such as:
- Printed circuit boards
- Connectors and switch contacts
- Bond wires for chip packaging
- Memory chips
- CPU processors
Medical Applications:
In healthcare technology, gold's biocompatibility and resistance to bacterial colonization make it invaluable. The metal finds applications in:
- Diagnostic devices for rapid testing
- Dental work and implants
- Cancer treatment through gold nanoparticles
- Medical imaging equipment
- Surgical instruments
Recent advances in nanotechnology have expanded gold's medical applications. Gold nanoparticles are being researched for targeted drug delivery systems and as contrast agents in medical imaging. Their ability to convert light into heat also makes them promising candidates for photodynamic therapy in cancer treatment.
Aerospace and Space Technology:
The aerospace industry relies heavily on gold for its protective and reflective properties. Spacecraft and satellites use gold-coated polyester film for thermal insulation, as gold efficiently reflects infrared radiation while allowing visible light to pass through. This characteristic helps maintain stable temperatures in the extreme conditions of space.
NASA and other space agencies utilize gold in:
- Astronaut helmet visors
- Satellite components
- Telescope mirrors
- Thermal protection systems
- Electrical connections in spacecraft
Environmental and Green Technology:
Gold's role in environmental technology is growing, particularly in:
- Catalytic converters for reducing vehicle emissions
- Fuel cells for clean energy production
- Solar panels for improved efficiency
- Water purification systems
- Air quality sensors
Research shows that gold nanoparticles can enhance the efficiency of solar cells by improving light absorption and electron transport. They also serve as effective catalysts in converting harmful carbon monoxide into carbon dioxide, making them valuable for air purification systems.
Future prospects and innovations:
The future of gold in technology looks promising with ongoing research into new applications. Scientists are exploring:
- Quantum computing components using gold connections
- Advanced medical diagnostic tools
- More efficient solar energy systems
- Flexible electronics and displays
- Enhanced battery technology
The development of new gold-based nanomaterials could revolutionize various technological fields. For instance, researchers are working on gold-based metamaterials that could lead to improved optical computing and more efficient telecommunication systems.
Economic and Environmental Considerations:
While gold's technological applications are valuable, the industry faces challenges regarding sustainability and cost. The rising demand for gold in technology competes with traditional jewelry and investment markets, potentially affecting prices and availability. Additionally, gold mining's environmental impact has led to increased focus on recycling and developing more sustainable extraction methods.
Conclusion
Gold's role in technology extends far beyond its decorative value. Its unique properties make it indispensable in modern electronic devices, medical equipment, and aerospace applications. As technology continues to advance, gold's importance in innovation is likely to grow, driving new discoveries and applications across various industries. The challenge lies in balancing the increasing technological demand for gold with environmental sustainability and economic considerations, ensuring this precious resource continues to benefit technological progress while minimizing its environmental impact.
The combination of gold's reliability, versatility, and unique properties ensures its continued significance in technological advancement, making it truly a precious metal for the digital age.

Our Promise
Fast shipping
Receive your jewelry in maximum 3 days.
Return guaranteed
Requesting a return is quick and easy.
Ethical Sourcing
Ethically Sourced Materials
Payments
Buy in the most convenient way for you.







